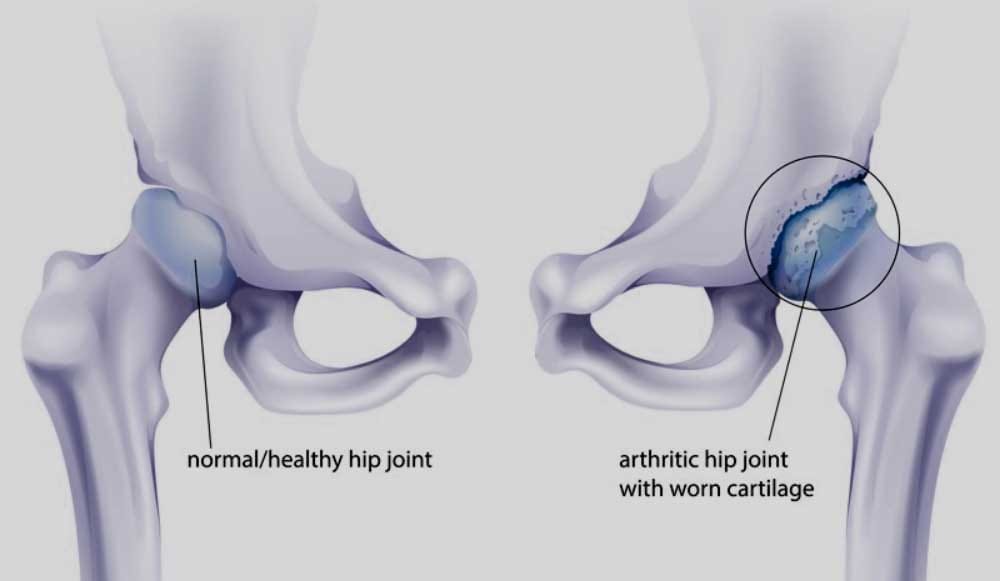
Osteoarthritis also called degenerative joint disease is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in older people. This disease affects the tissue covering the ends of bones in a joint (cartilage). In a person with osteoarthritis, the cartilage becomes damaged and worn out causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and restricted movement in the affected joint. Although osteoarthritis may affect various joints including hips, knees, hands, and spine, the hip joint is most commonly affected. Rarely, the disease may affect the shoulders, wrists, and feet.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by damaged articular cartilage, and cartilage lining the hip joint. Advanced age is one of the most common reasons for osteoarthritis of hip. You may also develop osteoarthritis if you had a hip injury or fracture in the past, if you have a family history of osteoarthritis, suffering from hip diseases such as avascular necrosis and other congenital or developmental hip diseases.
How do you know that you have osteoarthritis of the hip? The characteristic symptoms and diagnostic tests help in diagnosing the condition. You will experience severe pain confined to the hip and thighs, morning stiffness, and a limited range of motion. function-limiting hip pain, effect on walking distances, pain at night or rest, mechanical instability, locking, catching sensation, gait alteration, leg length discrepancy, and reduced range of motion in the form of;
- lack of full extension
- lack of full flexion
- limited internal rotation
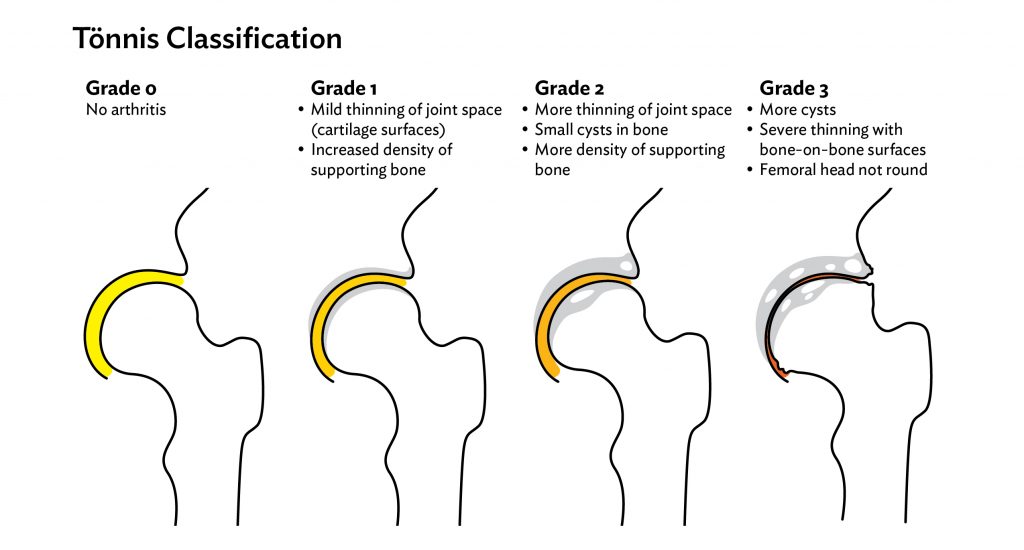
Based on the symptoms your orthopedic surgeon will perform a physical examination, X-rays and other scans to check for the grade of hip osteoarthritis.
Treatment
Initial treatment for osteoarthritis of the Hip is according to the grade. we have 3 grades of hip osteoarthritis. Grade 1,2, will benefit from conservative. In the form of:
- Weight control to reduce the stress on the joint and the use of analgesic and or anti-inflammatory medications to control the pain.
- Exercises to keep joints flexible and improve the strength of muscles around the hip. Studies have shown that exercise helps people with arthritis by reducing joint pain and stiffness and increasing flexibility, muscle strength, and energy. It also helps with weight reduction and offers an improved sense of well-being.
- Grade 3 when conservative measures have been exhausted and are no longer helpful, and arthritis has become disabling, surgery may be recommended in the form of total Hip replacement or partial Hip replacement.






