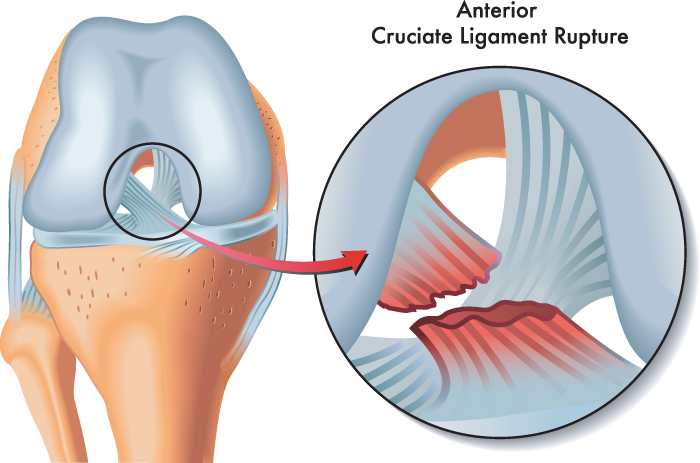
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear
The anterior cruciate ligament is a thick rope like structure made from collagen that joins the femur to the tibia.
Its main function is to provide rotational stability to a knee joint. The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the major stabilising ligaments in the knee. It acts as a strong brace.
Causes of ACL Injuries
ACL injuries are one of the most common ligament injuries in the body. Once the anterior cruciate ligament is torn it has a poor ability to heal and typically will not heal if untreated.
The ACL can tear with different types of injury such as:
- Twisting and rotational injuries, such as occur with a sudden change in direction or speed
- Contact injuries in collision sports or road accidents
- Hyperextension injuries
- Hyperflexion injuries
- An audible ‘pop’ sound from the knee
- A sensation of something tearing inside the knee.
- A feeling as if the knee has momentarily ‘come out of its joint’.
- Swelling of the knee
- Difficulty walking and
- Pain
- on uneven ground or
- Most ACL injuries are complete tears.
- Partial ACL tears
- History of injury
- Nature of knee pain and other symptoms
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests
- MRI scans will show the ACL tear as well as any meniscal or cartilage damage
- Knee instability
- Buckling of the knee
- Giving-way of the knee






